In ERAMON you can enter various Masterdata information. The following hierarchical structure is available.
Basic Module
Master Data Hierarchy
- Tenants
- Customer Groups
- Customers
- Locations
- Devices
- Ports
Permissions
Permissions determine which data can be seen and/or edited by which user. These permissions can be granted by administrators on the basis of permission groups or right down to the level of individual users.
The advantage of this is that you can define individual pages for specific requirements. Access to sensitive information can thus be restricted to the authorized group of people.
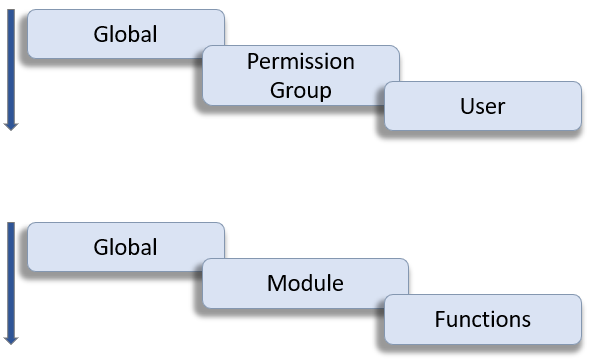
ERAMON Pemission Concept:
- Global Permissions
apply equally to all users. - Permission Groups
restrict or extend access rights for specific groups of people. - User
with special access or restriction. - Menus
can be tailored to the tasks to be performed, e.g. departments such as NOCs or finance.
- Special permissions
for groups and on user level complement the concept. These allow for special editing functions to be either enabled or hidden. - Permissions based on location groups
They include one or more locations, such as rooms, buildings, regions, etc. and allow the organization of rights on the basis of groups that are managed either automatically or manually.
Custom Fields
Custom fields are additional input and/or selection fields for ERAMON, which can be set up individually by the user. The fields can be specified as needed, for example text entry, drop-down lists, checkbox fields.
Among other options, a field’s content can be entered either automatically via SNMP or read out via L2 tracking, which is available for ports.
Once set up and depending on the assignment, a custom field is available for the following areas:
- Contacts
- Devices
- Customers
- Locations
- Ports
- Service Contracts
Device Import
Various options are available for the setup of devices:
- Device Importer: import via CSV files
- Auto-Scan: automatic scan of one or more IP networks
- Manual device import: GUI for setting up a device
- Interface: variable formats are available (XML, database, etc.)
Group Administration
Groups can be saved for many sections/functions to carry out specific operations effectively and in a standardized manner.
- Specifying a ruleset for automatically arranging devices in groups, for example based on the manufacturer’s name.
- Scheduled provisioning jobs based on device or port groups.
- Automatically add “Config Compliance” violations to a group where the focus is on their correction.
- Particular measurements in the Performance Management, such as QoS loads, can only be run for a specific port group.
Setting parameters with the help of rules
Use port and device rulesets that automatically run through a specified sequence and carry out settings. Rulesets are automatically carried out for new devices and thus reduce the need for manual effort to a minimum.
Practical examples:
Not all ports on the network are to be monitored, or performance data polled from them?
01.
1. Rule
02.
2. Rule
03.
3. Rule
04.
4. Rule
Specific SNMP parameters are to be set for certain devices, or the config backup activated?
- Activate the config back up for all “Cisco” devices.
- Also activate the firmware backup for all LAN-“Cisco” devices.
- Deactivate the firmware backup for all WAN-“Cisco” devices.
Both rulesets are run automatically for new devices, the system therefore manages itself.
Authentication
By default users are authenticated on the GUI via a local password. Depending on the application, this can be edited via the following protocols:
- RADIUS
- TACACS
- LDAP
The client ability allows you to record a separate authentication for each client.
Further Settings
Within the master data menu you are presented with a wide range of possible settings for device parameters, for example: an adjustable timeout for SNMP pollings or alternative Sys-OIDs, and more. For other sections/operations you are given a range of options via the configuration parameters, to customize ERAMON specifically for the user area. You could, for example, customize the display of the graphs.
This is just a selection of possible settings for the ERAMON application modules:
- Carrier Management
Technical parameters: These enable you to manage the technical parameters for the order of circuits, such as: interface, terminating unit, transfer unit. - Devices
Default setting of ports, default values of ports during the scanning process (managed, EPM), can be specified: all managed, all unmanaged, all ports with Oper status up, or all ports with admin status up. - EPM
Saving a logo in png-format as a background image in graphs. - Operations
Acknowledgement obligation: when acknowledging an event through the central event console, the user has to enter a text, such as a ticket number. - Provisioning
TACACS: When creating a job, the user has to enter a TACACS password. Alternatively, the system will use a super-user already existant in the background.
Display of RSS Feeds in ERAMON
The use of RSS feeds allows you to follow news and other dynamically developing content immediately, without the need to access the various websites each time you want an update.
With ERAMON you have the option to display RSS feeds in the following areas:
- as a quick link,
- in the Premium Reporting Dashboard which you can use as your ERAMON welcome screen,
- or as a separate menu entry.